What is KStream
A KStream is an abstraction of a record stream, where each data record represents in the unbounded data set. Using the table analogy, data records in a record stream are always interpreted as an “INSERT” – because no record replaces an existing row with the same key.
KStream can be created directly from one or many Kafka topics (using StreamsBuilder.stream) or as a result of transformations on an existing KStream.
val streamsBuilder: StreamsBuilder = new StreamsBuilder
streamsBuilder.stream[String,String]("input-topic")
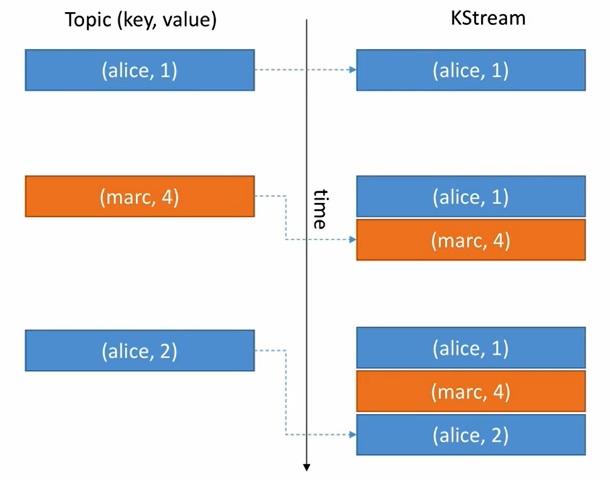
- Kstream is all inserts. Every data entered into Kstream as insert new entry for each and every record stream.
- Kstream is similar to log just a ordered sequence of mags like a topic.
- Kstream are infinite means unbounded data stream there is no end always expects more data to come.
Let’s undstand by below example first we have alice as a record and we inserted to KStream like same for marc as well. last we have alice again we inserted into KStream.
Operators supported by KStream:
KStream comes with a rich set of operators that allow for building topologies to consume, process and produce key-value records. below are the few operators. Check out the rich set of operators.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| Branch | Branch (or split) a KStream based on the supplied predicates into one or more KStream instances. |
| Filter | Evaluates a boolean function for each element and retains those for which the function returns true. |
| FlatMap | Takes one record and produces zero, one, or more records. You can modify the record keys and values, including their types. |
| FlatMapValues | Takes one record and produces zero, one, or more records, while retaining the key of the original record. You can modify the record values and the value type. |
| Map | Takes one record and produces one record. You can modify the record key and value, including their types. |
| MapValues | Takes one record and produces one record, while retaining the key of the original record. You can modify the record value and the value type. |
| GroupByKey | Groups the records by the existing key. |
| GroupBy | Groups the records by a new key, which may be of a different key type. When grouping a table, you may also specify a new value and value type. |
What is KTable
KTable is the abstraction of a changelog streamwhere each data record represents an update. Each record in the changelog stream is an update on the primary-keyed table with the record key as the primary key.
KTable assumes that records from the source topic that have null keys are simply dropped.
KTable can be created directly from a Kafka topic (using StreamsBuilder.table) or as a result of transformations on an existing KTable, or aggregations (aggregate, count, and reduce).
val streamsBuilder: StreamsBuilder = new StreamsBuilder
streamsBuilder.table[String,String]("input-topic")
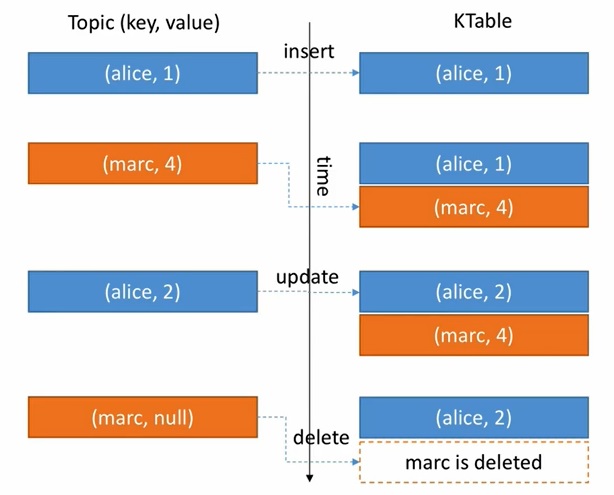
- KTable is all Upsert on non null values.
- KTable delete the record by null values if value is null, it will drop the record.
- KTables are equivalent to DB tables (Tables must use the PRIMARY KEY constraint), and as in these, using a KTable means that you just care about the latest state of the row/entity, which means that any previous states can be safely thrown away.
- If you store a KTable into a Kafka topic, you’d probably want to enable Kafka’s log compaction feature.
Let’s understand by below example first we have alice then it’s inserted into table same with marc. Next again we have alice now we update the table be new value. last we have marc with null value ktable simply drop the record.
Operators supported by KTable:
KTable comes with a rich set of operators that allow for building topologies to consume, process and produce key-value records. below are the few operators. Check out the rich set of operators.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| Filter | Evaluates a boolean function for each element and retains those for which the function returns true. |
| FilterNot | Evaluates a boolean function for each element and retains those for which the function returns false. |
| MapValues | Takes one record and produces one record, while retaining the key of the original record. You can modify the record value and the value type. |
| GroupBy | Groups the records by a new key, which may be of a different key type. When grouping a table, you may also specify a new value and value type. |
| join | Join the two KTable and produce the result |
The Stream Table Duality
In Apache Kafka, streams and tables work together. A stream can be a table, and a table can be a stream. It is a property of Kafka Streams with which we can achieve this versatility.
Because of the stream-table duality, we can easily turn a stream into a table, and vice versa. Even more, we can do this in a continuous, streaming manner so that both the stream and the table are always up to date with the latest events.
1) Table to Stream
A Table could be viewed as a stream, with the latest values for a particular field coming in. It’s just a snapshot of the latest values of a key in a stream at a given point in time.
We can turn a table into a stream_ by capturing the changes made to the table—inserts, updates, and deletes—into a “change stream.”
Example: To sometime helpful to transform a KTable to KStream inorder to keep a changelog of all the changes to the KTable.
val streamsBuilder: StreamsBuilder = new StreamsBuilder
val table:KTable[String,String]=streamsBuilder.table[String,String]("input-topic")
val stream:KStream[String,String]=table.toStream()
2) Stream to Table
A Stream could be viewed as table. A stream can be seen as a changelogs of a table. Where each data record in the stream captures a state change of the table.
We can turn a stream into a table_ by aggregating the stream with operations such as COUNT() or SUM()
Example: To sometime helpful to transform a KStream to KTable. by two ways we can create a KTable from KStream.
- Chain a groupByKey() and apply any aggregation step.
val streamsBuilder: StreamsBuilder = new StreamsBuilder val stream:KStream[String,String]=streamsBuilder.stream[String,String]("input-topic") val result:KTable[String, lang.Long]=stream.groupByKey().count() - Write back to kafka topic and read as a table.
val streamsBuilder: StreamsBuilder = new StreamsBuilder val stream:KStream[String,String]=streamsBuilder.stream[String,String]("input-topic") stream.to("intermediate-topic") val table:KTable[String,String]=streamsBuilder.table[String,String]("intermediate-topic")

Comments