What is Synapse SQL pool?
Synapse SQL Pool (formerly SQL Data Warehouse) is an MPP Enterprise Data Warehouse on Azure.
- Synapse SQL pool stores data in relational tables with columnar storage.
- Synapse SQL pool has compute separate from storage which enables to scale.
- Synapse Service Level Objective (Compute) is the scalability setting which determines cost and performance of the data warehouse (DWU). It ranges from DW100c to DW30000c, higher configuration has more nodes.
- Workload management is additional feature around managing resource utilization, concurrency and query priority.
- Synapse compute can be scale up down via SQL, PowerShell and Portal. The SQL ability for scaling is unique, and can be achieved via an “ALTER” command.
How organizations use the Modern SQL Data Warehouse ?
- If you want to independently size compute power regardless of your storage needs because the compute nodes and the storage nodes are kept separate.
- This way allows you can grow or shrink the compute power without moving that data. what you’re doing is you’re moving to compute node over to the data rather than moving all the date around, putting in one place, and then having to analyse it there. You can grow or shrink the compute power.
- You can pause your compute capacity while leaving data intact so this makes it so you only pay for the storage(storage is more cheaper than the processing).
- You can resume your compute capacity during business hours and start processing the data for reporting and etc.
Massive Parallel Processing (MPP Architecture)
In the Massive Parallel Processing at the top here we have the control node and this is the application or user connection. The control node is the brain/heart of your massive parallel processing engine.
It divides it up into 60 different nodes, and what this allows you to do processing in parallel to different nodes that you have of your storage. So what this is going to do is make a very powerful engine to run massive queries upon your data.
It’s also broken into different partitions that allow you to just look at and analyze separate pieces of your data as it is going along. Hence the name Massive Parallel Processing.
And at the bottom we have the Azure storage, this is where you keep your data, and it is separate from the compute power and save most of the cost.
Dedicated SQL Pool uses a node-based architecture. Applications connect and issue T-SQL commands to a Control node. The Control node hosts the distributed query engine, which optimizes queries for parallel processing, and then passes operations to Compute nodes to do their work in parallel. The Compute nodes store all user data in Azure Storage and run the parallel queries.
Serverless SQL Pool Control node utilizes Distributed Query Processing (DQP) engine to distributed execution of user query by splitting it into smaller queries that will be executed on Compute nodes. Each small query is called task and represents distributed execution unit. It reads file(s) from storage, joins results from other tasks, groups, or orders data retrieved from other tasks. The Compute nodes store all user data in Azure Storage and run the parallel queries.
Control node This is the front end that interacts with all applications and connections, and the MPP engine runs on the control node, and this optimizes and coordinates your parallel queries. When you submit a T-SQL query, the Control node transforms it into queries that run against each distribution in parallel.
Compute nodes provides a computational power for your analytics. It’s separated from the storage nodes, and you can scale this using what’s called Data Warehouse Units. As you pay for more compute resources, distributions are remapped to available Compute nodes. The number of compute nodes ranges from 1 to 60, and is determined by the service level for Synapse SQL.
Data Warehouse Units is a collection of analytic resources that are provisioned, and it’s basically a combination of CPU, memory and IO. And you can scale this up and you can scale this down depending upon what your needs are. A DWU, or Data Warehouse Unit, is the basic unit of these different resources, and you can add DWUs or subtracted DWUs.
Data Movement Service is the data transport technology that coordinates data movement between the Compute nodes. Some queries require data movement to ensure the parallel queries return accurate results. When data movement is required, DMS ensures the right data gets to the right location.
Storage Node (Azure Storage) and lastly, we have the storage node, and the storage node is kept separate from compute in order to keep data at rest. And this data at rest is cheaper than the data that is being analysed.
Implementing Data Distributions for SQL Data Warehouse
A distribution is the basic unit of storage and processing for parallel queries that run on distributed data. When Synapse SQL runs a query, the work is divided into 60 smaller queries that run in parallel. Each of the 60 smaller queries runs on one of the data distributions.
Three types of Distributions
-
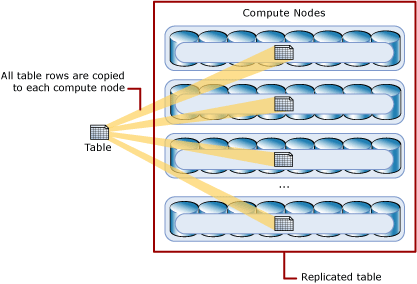
Replicated Table : A table that is replicated caches a full copy of the table on each compute node. Consequently, replicating a table removes the need to transfer data among compute nodes before a join or aggregation. Replicated tables are best utilized with small tables. Extra storage is required and there is additional overhead that is incurred when writing data.
A replicated table provides the fastest query performance for small tables.
-
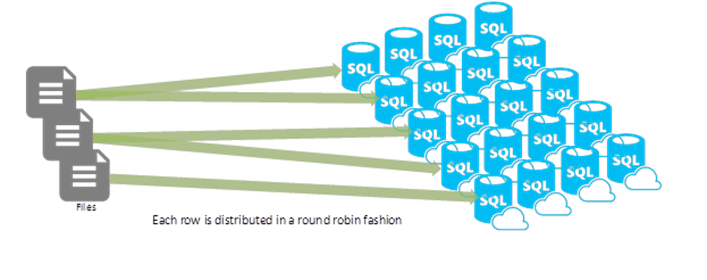
Round-robin Distributed Table : A round-robin distributed table distributes data evenly across the table but without any further optimization. A distribution is first chosen at random and then buffers of rows are assigned to distributions sequentially. It is quick to load data into a round-robin table. Joins on round-robin tables require reshuffling data, which takes additional time.
A replicated table provides the fastest query performance for small tables.
-
Hash Distributed Table : This uses a hash function to assign each row to one distribution or node. In the table definition, one of the columns is designated as the distribution column. The hash function uses the values in the distribution column to assign each row to a distribution.
A hash distributed table can deliver the highest query performance for joins and aggregations on large tables.

what data distribution to use?

Implementing partitions for SQL Data Warehouse
- Table partitions enable you to divide the data into smaller groups of data to make it more functionable when you’re dealing with a large amount of data.
- You can improve the efficiency and the performance of loading data by use of partition deletion, switching, and merging. So depending upon how you partition your data, you can load just the data that you need.
- It can also be used to improve query performance by just focusing on the data that you want a query and not having to bother searching through all the data that you don’t want to query.
Three types of Partitioning
- Clustered Columnstore : The Clustered Column store, and that’s updatable primary storage method, and it’s great for read‑only.
- Clustered Index : The Clustered Index, and that index is physically stored on the same order as the data being indexed. So a Clustered Index requires order.
- Heap : To use Heap where data is not in any particular order, and it’s best used when data does not have a natural order to it, then you should use a heap.
Next ?
Planning to create multiple blogs episodes on azure synapse covering various areas related to azure synapse and showing you the way of using these services for implementing your data warehouse solution.


Comments